Full Spectrum Grow Lights vs Targeted-Spectrum Grow Lights
When Mars Grow Lights revolutionized the grow light industry in 2013,We changed the way farming works.

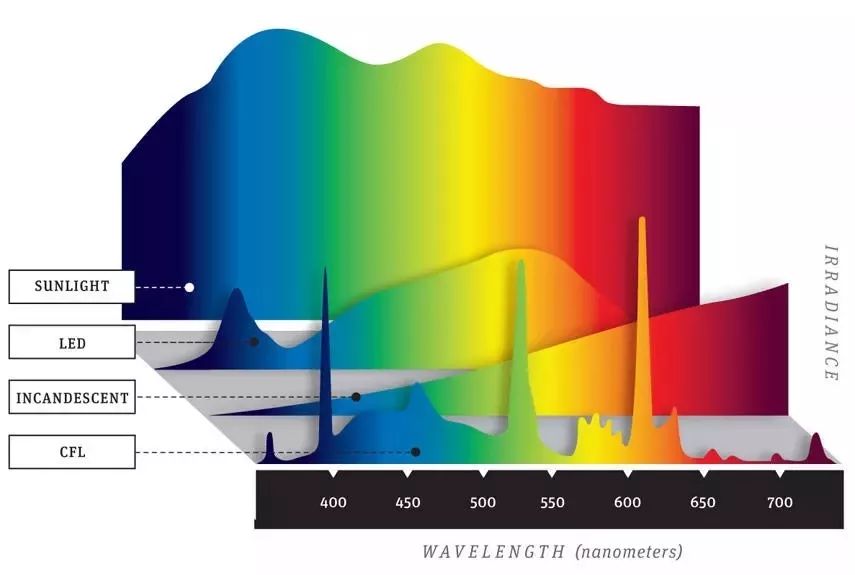
| Effects of Light Color | Wavelength | on Plants |
| Blue Light Spectrum | 400 500 nm | Stimulates chlorophyll production Promotes vegetative growth, leaf development, stem elongation and root growth Allows more carbon dioxide to enter leaves Enhances photosynthesis efficiency Faces plant growth to light sources Strict management of growth cycles |
| Red Spectrum | 600 700 nm | Triggers the transition from vegetative to reproductive growth Stimulates the production of flowering hormones to initiate the flowering process Promotes flower and fruit development Affects seed germination |
| Green Spectrum | 500 600 nm | Less effective than red and blue light Helps penetrate deep into the plant canopy It can reach the lower leaves of plants to help them photosynthesize |
| Far Red Spectrum | 700-850 nm | Stem elongation Leaf expansion and flowering start-up affect seed germination control plant height and flowering time improve fruit yield of short-day plants |
| Orange Spectrum | 590-620 nm | Promote plant photosynthesis affect plant movement |
| Yellow Light Spectrum | 570-590 nm | Minimal photosynthetic activity is similar to the orange spectrum |
| Ultraviolet (UV) Spectrum | UV-A (315-400 nm) | Modulate various physiological processes to enhance the production of secondary metabolites |
| UV-B (280-315nm) | Has positive and negative effects on plants Stimulate the production of certain secondary metabolites affect plant morphology, excessive UV-B can damage DNA | |
| UV-C (100-280 nm) | Not conducive to Plant/horticultural purposes may cause serious damage to plant tissues |
MarsGrow Full Spectrum LED Growth Light
The distance between LED grow lights and plants
The distance between the LED grow light and the plants is critical to maintaining light intensity. If the light is too far away from the plant, the plant won't get enough light to activate photosynthesis. Likewise, placing fixtures too close together can negatively affect plant growth. This is why proper lighting distance is a must. But for different plant growth stages, the requirements for this distance are different. These are as follows-
-
Seedling stage: The seedling stage of plants requires lower light intensity. In this case, the distance of the LED grow lights should range from 24-36 inches from the top of the soil. Soft light from this distance will help them germinate properly.
-
Plant growth stage: The growth stage of plants requires stronger light to ensure normal growth. Therefore, the distance between the light and the plants should be shortened; a 12-24 inch range is ideal. This will help the plant photosynthesize and promote faster growth.
-
Flowering and fruiting stages: More intense lighting is required to support the flowering and fruiting stages. Lighting distance of 16-36 inches from the plant canopy results in better yields.
Note: The recommended distance between LED grow lights and plants may vary based on the size and light intensity of the fixture.
Learn about watts
The wattage rating of a light determines its intensity. Higher wattage means brighter light output. Since different plants have different requirements for light intensity, different plants also have different wattage requirements for LED lights. Generally, flowering plants require more wattage than fruiting plants. Below I have added a table of LED grow light wattage recommendations for your convenience
| Wattage Recommendations for Different Types of Garden Plants | ||
| plant type | For example: | Recommended wattage |
| Green leafy vegetables and herbs | Lettuce, spinach, basil and other leafy green vegetables | 20-30 watts per square foot |
| fruit vegetables | tomatoes, peppers and cucumbers | 30-40 watts per square foot |
| flowering plant | Roses, Orchids and Annuals | 40-50 watts per square foot |
| High light plants | marijuana | 50 watts per square foot or more |
Note: The image above shows general recommendations. Before choosing an LED grow light wattage, consider your plant type and analyze its lighting requirements.

Heat dissipation
Overheating of LED lamps can damage the LED chips. In addition, if the LED grow lights emit too much heat, it will hinder the natural activities of the plants. However, LED grow lights with high-quality heat sinks can solve this problem. Check out this article to learn more about heat sinks - LED Heat Sink: What is it and why is it important? Additionally, there are some other factors that you should consider; these are-
-
Buy LED grow lights with fans; they help minimize heat emissions.
-
Consider liquid cooling or thermoelectric cooling in your grow lights.
-
Choose a well-designed LED grow light to ensure that the heat emitted is distributed throughout the fixture.
IP rating
When LED grow lights are placed in a garden area, they handle a large amount of moisture. Plants release large amounts of water through the process of transpiration. This allows indoor gardens to maintain a higher humidity level. Additionally, the garden environment involves soil, fertilizer, and dust particles. Therefore, the IP rating is an important consideration in ensuring that your fixtures are protected from this environment. Generally, IP65 is considered best for LED grow lights. This protects the fixture from dust, dirt and moisture. For information about IP ratings, you can read IP Ratings: The Definitive Guide.

How long should grow lights be on?
The duration that your grow lights are on depends on the plant’s photoperiod. Now what is photoperiod? Photoperiod refers to the day length, or duration of each day, when plants absorb light. The photoperiod of all plants is not the same. For example, short-day plants don't require much sunlight throughout the day. In these plants, the nights are longer. Most winter plants are short-day plants. Likewise, for long-day plants, longer lighting periods are required. That means you need to keep your LED grow lights on longer.
| Photoperiod based on plant type | ||
| plant type | For example: | photoperiod |
| short day plants | Chrysanthemums, Kalanchoe, Rhododendrons and Begonias | 12 hours a day |
| long day plants | Vegetable and garden flower seedlings | 18 hours a day |
Likewise, light duration also changes with the growth stage of the plant. Typically, plant growth stages are divided into three groups: seeding, vegetative, and flowering/fruiting. The lighting time for each stage is as follows:
| Photoperiod of plants at different growth stages | |
| growing phase | During the lighting period |
| Seedling stage | 14 to 16 hours of light per day |
| vegetative stage | 14 to 18 hours of light per day |
| Flowering and fruiting period | 12 hours of light per day |

.jpg)