LED Heat Sink: What is it and why is it important?
To ensure the proper operation of the LED and the thermal management system, it is necessary to install an appropriate heat sink, which will enable the device to last longer.
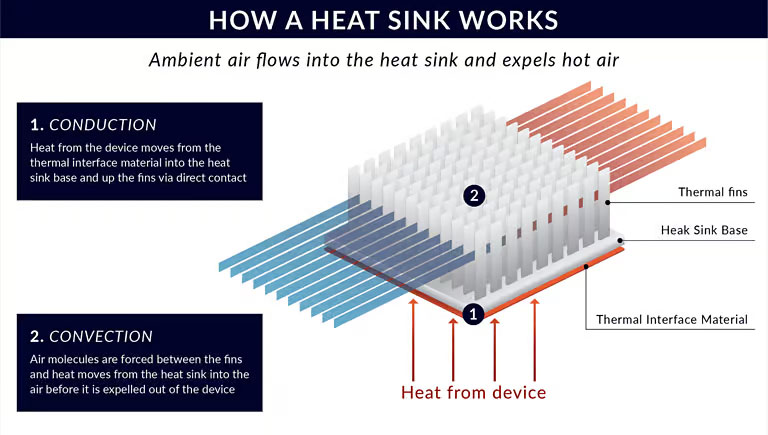
How does an LED heat sink work?
- generate heat
When an LED light source is powered, it generates heat as a by-product of light emission.
- heat transfer
The heat generated is transferred from the LED chip to the metal core printed circuit board (MCPCB) or heat sink.
- Heat dissipation
The heat sink is the thermal bridge between the LED chip and the surrounding environment. It conducts heat from the LED chip to the air. In addition, the large surface area of the heat sink provides ample space for heat dissipation.
- Heat radiation
Radiators dissipate heat into the surrounding environment through a combination of convection and conduction. Heat moves from the hot surface of the radiator to the cooler air. It creates a temperature difference that dissipates heat away from the LED chip.
- LED cooling
The LED chip temperature decreases as heat is dissipated, preventing overheating. It allows LEDs to operate at safe and efficient temperatures. The heat sink also helps prevent damage to the LED chips due to overheating.
Heat sink materials: Aluminum vs. Copper – which one is better?
Aluminum and copper each have their own pros and cons. Therefore, it is crucial to understand their differences to make an informed decision.
| Aluminum radiator | Copper heat sink |
| Light weight and low cost | Heavy and expensive compared to aluminum |
| High thermal conductivity | High thermal conductivity |
| Low mechanical strength | High mechanical strength |
| Not as conductive as copper | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity |
Aluminum has a lower thermal conductivity than copper, which means heat takes more time to move through it. Aluminum, on the other hand, is significantly lighter than copper and has greater structural integrity.
Additionally, copper conducts heat better than aluminum. This makes it a better choice for applications that require the most efficient cooling. Additionally, copper does not corrode like aluminum.
Ultimately, which material is better depends on the specific needs of the application. For industrial lighting and automotive lighting, copper is best. Aluminum, on the other hand, is a perfect choice for architectural lighting.
MCPCB: How does it help LED heat sinks?
MCPCBs are metal core A printed circuit board . They are designed to efficiently dissipate LED heat away from the light source. The metal core of MCPCB acts as a thermal bridge. This allows heat to dissipate from the LED to the heat sink.
MCPCB technology takes advantage of the fact that metal has a much higher thermal conductivity than FR4 (fiberglass reinforced epoxy). Therefore, it can move heat away from the LED more efficiently. The metal core also provides structural stability. It improves electrical connectivity, making it an ideal solution for LED cooling applications.
Do LED light strips need a heat sink?
Small, low-power LED light strip usually don't require a heat sink because they generate very little heat. However, for high-power LED strips, a heat sink is highly recommended. Because it helps dissipate heat and prevent damage to the LED strip.
Radiators are usually made of metal and serve as conductors. It takes heat away from the LED strip and dissipates it into the surrounding air. Without a heat sink, high-power LED strips can overheat. This will shorten their lifespan and cause them to fail. Therefore, if you are using a high-power LED light strip, it is recommended to use a heat sink. This will ensure its longevity and optimal performance.
How to determine the heat sink size for a light strip?
Sizing the heat sink for your light strip is a critical step in the longevity and efficiency of your lighting system. Here are the steps for sizing your strip light heat sink:
Step-1: Determine the power of the light strip
The first step is to determine the wattage of the light strip in watts. This information is usually provided in the product specifications.
Step 2: Calculate the heat generated
The next step is to calculate the heat generated by the light strip. This can be done using the following formula: Heat generated = Power x Efficiency. The efficiency coefficient is usually around 90%.
Step 3: Determine the Heat Sink’s Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance is a measure of a heat sink's resistance to heat transfer. Usually expressed in °C/W.
Step 4: Determine the maximum allowable temperature rise
The maximum allowable temperature rise is the difference between the ambient temperature and the maximum temperature that the light strip should reach. Manufacturers usually specify this temperature.
Step 5: Calculate required heat sink size
The final step is to calculate the required heat sink size using the following formula -
Required heat sink size = heat generated ÷ (thermal resistance x maximum allowable temperature rise)
It's important to remember that the calculations above are only estimates. For a precise estimate, you can consult an expert. Also, consider the physical size of the heat sink. These are the length and width to ensure it fits the lighting system.

Factors to consider when choosing an LED heat sink
Factors that should be considered when choosing an LED radiator are as follows:
Thermal resistance
Thermal resistance refers to the heat sink's ability to dissipate heat away from the LED. If the thermal resistance is too high, heat can build up and cause the LED to overheat and fail prematurely.
On the other hand, if the thermal resistance is too low, the heat sink will be too bulky. This will affect the overall design of the LED system. Thermal resistance must be balanced against other factors such as cost, size, and materials to select the right LED heat sink for your specific application.
heat flow
When selecting an LED heat sink, consider heat flow. The main function of the heat sink is to dissipate heat from the LED. It prevents overheating and extends its life . If the heat sink cannot transfer heat efficiently, the LED will eventually overheat and fail.
You should evaluate heat flow based on the LED's power output. It also depends on the ambient temperature and the thermal resistance of the material. It is recommended to choose a radiator with high thermal conductivity and low thermal resistance. This will ensure optimal heat transfer. With proper heat flow, an LED heat sink will provide reliable and efficient cooling of the LEDs.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to transfer heat from one point to another. High thermal conductivity means heat will be efficiently dissipated from the LED to the heat sink. Use a heat sink with better thermal conductivity to prevent the LED from overheating. However, different materials have different thermal conductivity capabilities. For example, the thermal conductivity of aluminum ranges from approximately 170-251 W/mK. At the same time, copper has a higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, about 401 W/mK.
The perfect type of radiator
Passive heat sinks are designed to dissipate heat through natural convection and conduction. Therefore, they do not rely on active cooling methods such as fans or water cooling. This may be an attractive option for some applications as it eliminates the need for maintenance and noise. It also prevents potential failure points associated with active cooling. Additionally, passive heat sinks may be more cost-effective. It also has a smaller form factor than dynamic cooling solutions.
Natural convection
Natural convection is the transfer of heat through a fluid, usually air. During this process, the fluid/air flowing through the warm radiator removes heat from the surface and transfers it to the surrounding environment.
However, increasing air turbulence between radiator fin spacing greatly enhances natural convection. In this case, fin/plate design and construction are important. For example, fins with drilled holes speed up the cooling mechanism. So, consider this factor before choosing the ideal heat sink for your LEDs.
High heat dissipation
High heat dissipation allows LED lights to operate at lower temperatures. It reduces the risk of damage due to overheating and extends the life of the lamp. This type of heat sink reduces the energy required to cool the lamp. In turn, it reduces overall energy consumption. Additionally, high heat dissipation radiators help reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Fin shape and size
The size and number of heat sinks will determine the surface area for heat dissipation. At the same time, the shape of the fins affects the airflow and overall efficiency of the radiator. Additionally, a heat sink with large, evenly spaced fins will provide better heat dissipation. Compared to those with small, closely spaced fins. Additionally, the shape of the fins, such as flat or curved, can also affect heat dissipation performance.
common problem
